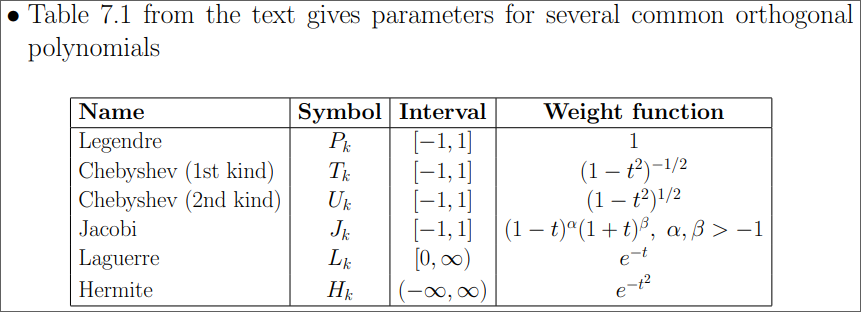
Concept
basically in order to use orthogonal polynomial for interpolation, we setup the orthogonal polynomial coefficient matrix with selected polynomials and solve it for coefficients.
Or we can use
where is the selected polynomial. Then
where is weighted inner-product.
interpolation error
where
Crude Error
assume we have
where and is constant with .
Code
import numpy as np
def T(j, x):
"""Compute Chebyshev polynomial T_j(x) = cos(j * arccos(x))"""
return np.cos(j * np.arccos(x))
def chebyshev_interp(f, n, t):
"""
Use Chebyshev polynomials T_j(x) and Gauss-Chebyshev quadrature
to interpolate function f on interval [-1, 1].
f: function to interpolate
n: number of basis functions
t: array of evaluation points
"""
# chebyshev_nodes
x_nodes = np.empty(n)
for i in range(n):
x_nodes[i] = np.cos((2 * i + 1) * np.pi / (2 * n))
f_vals = np.empty(n)
for i in range(n):
f_vals[i] = f(x_nodes[i])
coeffs = np.empty(n)
for j in range(n):
num = 0
denom = 0
for i in range(n):
Tij = T(j, x_nodes[i])
num += f_vals[i] * Tij
denom += Tij * Tij
num *= np.pi / n
denom *= np.pi / n
coeffs[j] = num / denom
res = np.empty_like(t)
for i in range(len(t)):
s = 0
for j in range(n):
s += coeffs[j] * T(j, t[i])
res[i] = s
return res